Tutorial
MiGA’s mainframe has 2 tabs. The first tab named “Ensembl or local” implements SSR search for organisms included at ensembl biodatabase. The second tab named “File from User” implements SSR search for FASTA file chosen by user.
“Ensembl or local”
In that case, choose the organisms (one or more) you want to analyse and then click on the button “Check last updated”.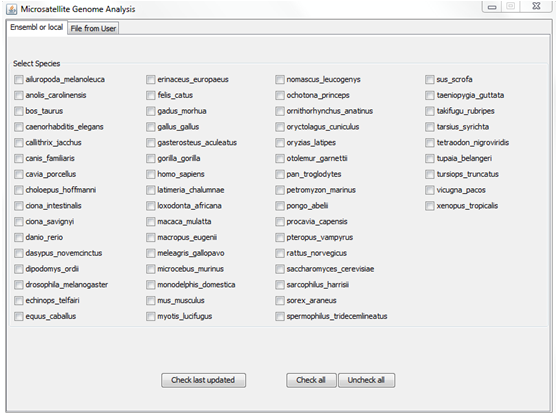
In the next window, there is a list with the organisms chosen before. For each one of them, there is either a timestamp with the date and time from the last update in the local database, or a message indicates that the organism have to be updated before proceed. If every organism chosen is updated (not red colour) and you wish to proceed, just avoid the next paragraph.
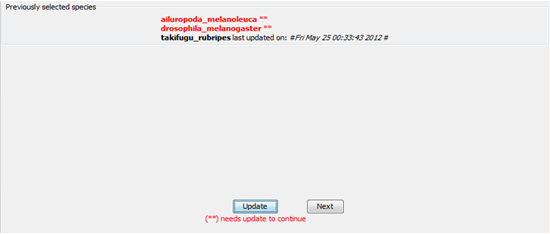
CAUTION! Internet connection is necessary for this step. If you choose Update, the program asks to choose those organisms you want to update. You can choose to update every organism you want even if it is already updated, but it is wise to do that only if the timestamp is really old because the update operation requires several hours. Choose the checkbox for each organism you want to update, click on the button “Update” and let the program update your local database. CAUTION!! You can minimize the window but under no circumstances should you close the window, the internet connection or the computer. After minimizing the window – during update – the window will appear black until the end of the update. There is no reason to worry about, the program continues execution normally and will proceed to the next frame as long as he update is completed. Updating speed depends on the internet connection’s speed and the computer’s abilities. Update might need several hours to complete. As soon as the update is completed, the previous window will show up and you can now choose the “Next” button. Once every chosen organism have been updated, you can proceed analysing their genome in order to find SSR’s in that.
“File from User”
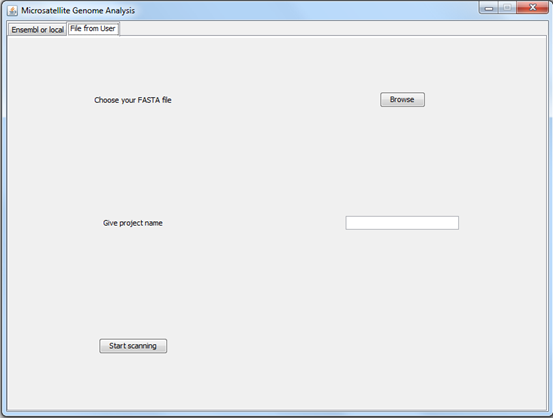
In this tab, you can choose the FASTA file you want to analyse. Click on the “Browse” button and choose the file. Then, give a project name and click on “Start scanning” button. Once file scanning is completed the next window will show up.
The final window of the program has 2 tabs. This window will appear either you have initially chosen “Ensembl or local” tab or “File from User” tab. In the first tab named “Statistics” the user have to insert the parameters according to which the program will search the genome for SSRs. The second tab, named “Sequence Retrieval” returns the SSR’s sequence along with it’s flanking regions.
Statistics
The main choices on this tab are:
- Perfect
- Imperfect
- Compound
- Perfect Compound
- Imperfect Compound
 If choices 1. Perfect or 2. Imperfect have been selected it is necessary to choose the Motif/Period (Mono-Di-Tri-Tetra-Penta-Hexa nucleotide) of the microsatellites SSRs.
If choices 1. Perfect or 2. Imperfect have been selected it is necessary to choose the Motif/Period (Mono-Di-Tri-Tetra-Penta-Hexa nucleotide) of the microsatellites SSRs.
More specifically for each SSR type chosen:
Perfect
In case perfect SSRs are chosen it is necessary to fill in the minumum SSR length (bp – base pair).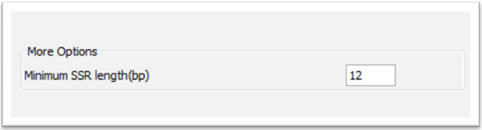
Imperfect
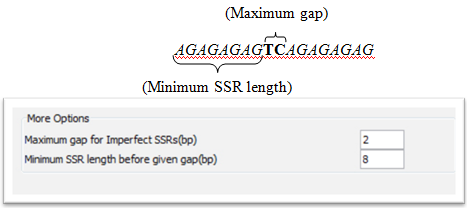
In case imperfect SSRs are chosen it is necessary to fill in the maximum gap for imperfect SSRs (bp – base pair) and the minimum SSR length before the given gap (bp – base pair).
E.g. Maximum gap for imperfect SSRs: 2 bp
Minimum SSR length before given gap: 8 bp
Compound Perfect/Imperfect
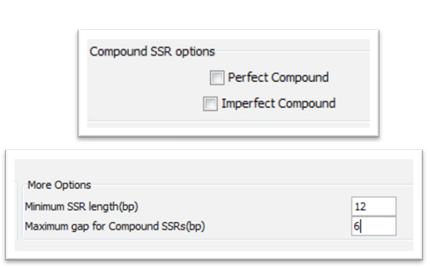 In case compound SSRs are chosen you have to choose the type of the compound SSRs you are seeking for (Perfect/Imperfect Compound).After that, it is necessary to fill in the minimum SSR length (bp – base pair) and the maximum gap for compound SSRs (bp – base parameters.
In case compound SSRs are chosen you have to choose the type of the compound SSRs you are seeking for (Perfect/Imperfect Compound).After that, it is necessary to fill in the minimum SSR length (bp – base pair) and the maximum gap for compound SSRs (bp – base parameters.
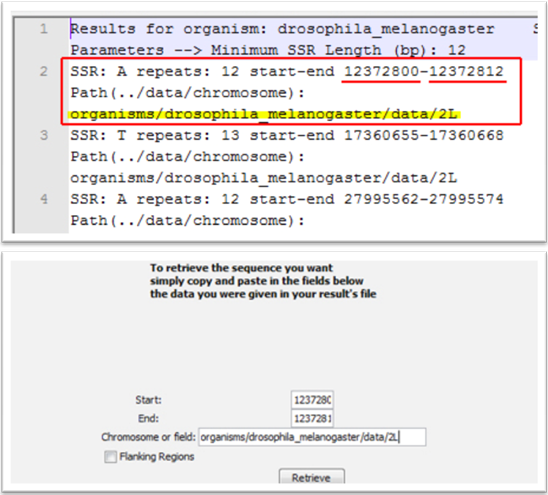
Once select search parameters click on the “Run” button and wait for a few minutes until results are shown. One .txt file opens in which you can see all the wanted SSRs found with information about their period (for perfect SSRs), their start and end base pair in the genome as well as the Path (see Sequence Retrieval). In addition, in the program’s folder there is now a folder named organisms including folders for each one of the organisms you have selected. In every one of them there is a folder named results with the results file produced. Besides that, there is also one folder named stats with the statistical representation (summary statistics) for each one of the organisms chosen.
Sequence Retrieval
This is the other tab on the final window. You can fill in Start, End, and Path (Chromosome or field) fields for one SSR that has been found and the program produces SSR’s sequence for any use (e.g. primers design etc.). More specific, copy and paste the information from the results file into the fields and then click on the “Retrieve” button. There is also an option with which you can retrieve flanking regions along with the SSR.